Novobiocin Susceptibility Test
for differentiating of Staphylococcus spp.
which included a novobiocin disk test.

Principle
Susceptibility
to novobiocin is determined by placing a novobiocin-impregnated
paper disk on a agar plate seeded with the organism under
investigation. As the organism multiplies during incubation to produce a lawn
of confluent growth, cells are exposed to the antibiotic diffusing into the
agar from the paper disk. If the bacteria are susceptible to novobiocin, there
will be a formation of visible zone of inhibition around the disk,
representing an area where the antibiotic concentration has prevented bacterial
growth. No zone of inhibition around the disk represents that organism is resistant
to the anitibiotic.

Novobiocin Disc:
Disk is prepared by
impregnating 5ug of novobiocin onto high quality 6mm diameter filter paper
disks (commercially available).

Method


1. The test isolate should be 18-72 hours and in
pure culture. Prepare a suspension of the test isolate in tryptic soy broth
equal to a McFarland 0.5 standard or equivalent.
2. Immerse a sterile swab into the suspension and
rotate it against the side of the tube above the fluid level to remove excess
inoculum.
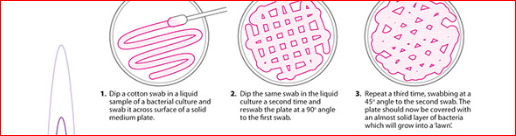
3. Using the expressed swab, inoculate a blood
agar or Mueller Hinton agar plate by streaking the swab over the entire agar
surface and repeat in 2 planes.
4. Allow the agar surface to dry no more than 15
minutes before applying a Novobiocin Disk. With a sterile swab, prepare a lawn
of growth over the entire plate by swabbing over the entire plate in 3
directions and around the edge of the plate.
5. Using alcohol-dipped and flamed forceps,
aseptically apply a novobiocin antibiotic disc to the surface of each
inoculated plate. Gently press the discs down with sterile forceps to ensure
that they adhere to the agar surface.
6. Incubate plate aerobically for 18 to 24 hours
at 35 to 37°C.
7. Measure the diameter of the zone of inhibition
using sliding calipers or a metric ruler.
Expected Results
- Positive – A zone of inhibition greater than 16mm indicates that
the organism is sensitive to the antibiotic.
- Negative – A zone of inhibition less than or equal to 16mm is
indicative of novobiocin resistance.
Staphylococci aureus
|
Staphylococci epidermidis
|
Staphylococci saprophyticus
|
|
Coagalase
|
(+)
|
(-)
|
(-)
|
MSA
|
(+)
|
(-)
|
(-)
|
AST( Novobiocin)
|
S
|
S
|
R
|
Limitations
- Testing should be performed on
isolated colonies of
aerobic, catalase-positive, coagulase-negative gram positive
cocci.
- It is recommended that
biochemical, immunological, molecular, or mass spectrometry testing be
performed on colonies from pure culture for complete identification.
- The novobiocin disk is not
helpful and can give misleading results if it is performed on isolates
other that those from urinary specimens.
- Occasional human isolates that
are not S. saprophyticus, S. cohnii subsp., or S.
xylosis may also be resistant to novobiocin
References
www.time2026end.com
Comments