Bacitracin Susceptibility Test
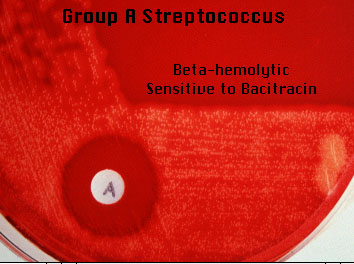
- The test is used for
presumptive identification and differentiation of beta-hemolytic group A
streptococci (Streptococcus pyogenes–
susceptible) from other beta-hemolytic streptococci.
- It is also used to distinguish
staphylococci species (resistant) from micrococci (susceptible).
Method
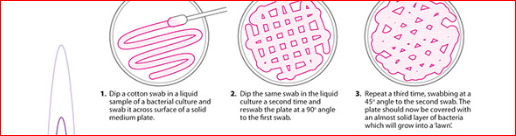
1. Using an inoculating loop, streak two or three
suspected colonies of a pure culture onto a blood agar plate.
2. Using heated forceps, place a bacitracin disk
in the first quadrant (area of heaviest growth). Gently tap the disk to ensure
adequate contact with the agar surface.

3. Incubate the plate for 18 to 24 hours at
35°-37°C in ambient air for staphylococci and in 5% to 10% carbon dioxide (CO2)
for streptococci differentiation.
4. Look for a zone of inhibition around the disk.
Medium Used:
Mostly, blood agar
plate is used (trypticase soy agar + 5% sheep blood).
Expected Results
- Positive: Any zone of inhibition greater than 10 mm;
susceptible.
- Negative: No zone of inhibition; resistant
Interpretation
- Performance depends on the
integrity of the disk. Proper storage and expiration dates should be
maintained.
- Culture media must be freshly
prepared for optimum diffusion of the antibiotic.
- Lancefield groups C and
G streptococci may occasionally also show susceptibility to
bacitracin.
- When testing isolates, a light
inoculum may result in false zone of inhibition.
References
www.time2026end.com
Comments