
Mannitol Salt Agar
(MSA) is used as a selective and differential medium for the isolation and
identification of Staphylococcus aureus from
clinical and non-clinical specimens. It encourages the growth of a group of
certain bacteria while inhibiting the growth of others. It is a selective
medium prepared according to the recommendations of Chapman for the isolation
of presumptive pathogenic staphylococci.
Composition of Mannitol Salt Agar
| Sodium Chloride | 75.0gm |
| Proteose Peptone | 10.0gm |
| Mannitol | 10.0gm |
| Beef Extract | 1.0gm |
| Phenol Red | 0.025gm |
| Agar | 15.0gm |
Distilled Water = 1000 ml
Final pH 7.4 ± 0.2 at
25°C.
Principle of Mannitol Salt Agar
Mannitol Salt Agar
contains peptones and beef extract, which
supply nitrogen, vitamins, minerals and amino acids essential for growth. The
7.5% concentration of sodium chloride results
in the partial or complete inhibition of bacterial organisms other than
staphylococci. Sodium chloride also supplies
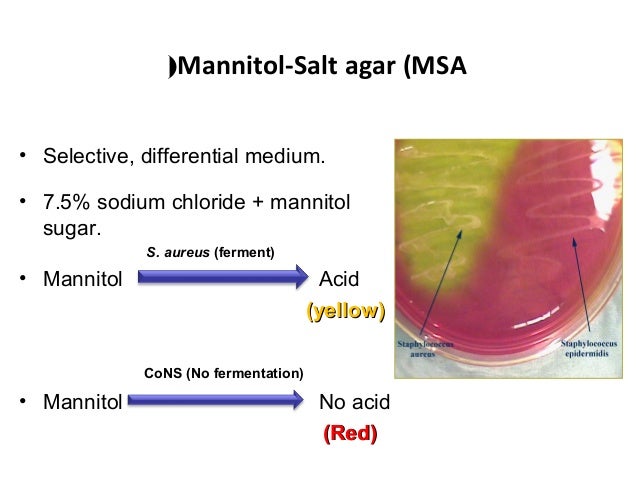
essential electrolytes for transport and osmotic balance. Mannitol is the fermentable carbohydrate,
fermentation of which leads to acid production, detected by phenol red indicator, aids in the differentiation
of staphylococcal species. Coagulase
test positive staphylococci (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus) produce yellow colonies and a
surrounding yellow medium while coagulase negative staphylococci produce red
colonies and no color change of the phenol red indicator. Agar is the solidifying agent.
Uses of Mannitol Salt Agar
1. It is used for the selective isolation and
differentiation of Staphylococcus aureus from
clinical samples.
2. It is also used for the enumeration of
staphylococci in food and dairy products.
3. This medium is also included in the
Bacteriological Analytical Manual for cosmetics testing.
4. It is also used in the bacteriological
examination of swimming pool water, spas and drinking water using membrane
filtration
Preparation of Mannitol Salt Agar
1. Suspend 111.025 gm of MRS media in 1000 ml of
distilled water.
2. Boil to dissolve the media completely.
3. Autoclave at 121°C for 15-20 minutes.
4. Cool to 45-50°C and pour into petri dishes.

Prepare culture
culture medium 18-24h
subculture to dividing staphylococci aureus between staphylococcus other and bacterial no grow on culture medium are high salt concentration .

Result Interpretation on Mannitol Salt Agar
Organisms
|
Results
|
Staphylococcus aureus
|
Yellow colonies with yellow zones.
|
Staphylococci other than S. aureus (e.g. Staphylococcus epidermidis ) and Bacillus anthracis
|
Colorless or Red colonies with red zones.
|
Streptococci
|
No growth to trace growth.
|
Micrococci
|
Large white to orange.
|
Gram-negative bacteria
|
No growth to trace growth.
|
Quality Control on Mannitol Salt Agar
Positive Control: Staphylococcus aureus ATCC
6538, Medium-sized yellow colonies
Negative Control: Escherichia coli ATCC
25922, Partial to Complete Inhibition.
Limitations of Mannitol Salt Agar
1. Several Staphylococcus species
other than aureus are mannitol positive
and produce yellow colonies surrounded by yellow zones on this medium
(e.g. S. capitis, S. xylosus, S. cohnii, S. sciuri, S. simulans,
and other species). Therefore, further biochemical tests are necessary for the
identification of S. aureus or other species.
2. Most organisms other than staphylococci are
inhibited by the high salt concentration found in Mannitol Salt Agar except for
some halophillic marine organisms.
3. A few strains of Staphylococcus aureus may exhibit a delayed
fermentation of mannitol. Negative plates should be re-incubated overnight
before discarding.
4. Presumptive Staphylococcus aureus must
be confirmed with a coagulase test.
References
www.time2026end.com
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mannitol_salt_agar
Mannitol Salt Agar. PML Microbiologicals, Inc.
Mannitol Salt Agar. Acumedia Manufacturers,
Inc.
Mannitol Salt Agar. Difco™ & BBL™ Manual,
2nd Edition
Mannitol Salt Agar. Liofilchem SRL.
Comments